
- Wireshark https vs http how to#
- Wireshark https vs http free#
- Wireshark https vs http mac#
Observe the encrypted handshake message. Expand Secure Sockets Layer, TLS, Handshake Protocol, and Encrypted Handshake Message to view SSL/TLS details. Select the fourth TLS packet, labeled Client Key Exchange, Change Cipher Spec, Encrypted Handshake Message. To analyze SSL/TLS Client Key Exchange traffic: This is the client TCP acknowledgement of Select the next TCP packet, labeled TCP ACK. The client uses the certificate to validate the public key and signature. Expand TLS, Handshake Protocol, and EC Diffie-Hellman Server Params to view the public key and signature.  Observe the certificate information provided. Expand Secure Sockets Layer, TLS, Handshake Protocol, and Certificates to view SSL/TLS details. Select the third TLS packet, labeled Certificate, Server Key Exchange, Server Hello Done. Observe the packet details in the middle Wireshark packet details pane.Īctivity 6 - Analyze SSL/TLS Certificate Traffic. Select the second TLS packet, labeled Server Hello. This is the server TCP acknowledgement of receiving the Client Hello request.Īctivity 5 - Analyze SSL/TLS Server Hello Traffic Select the next packet, labeled TCP ACK. Observe the Cipher Suites and Extensions supported. Expand Secure Sockets Layer, TLS, and Handshake Protocol to view SSL/TLS details. Also notice that the Ethernet II, Internet Protocol Version 4, and Transmission Control Protocol values are consistent with the TCP connection analyzed in Activity 3. Notice that it is an Ethernet II / Internet Protocol Version 4 / Transmission Control Protocol / Secure Sockets Layer frame. Observe the packet details in the middle Wireshark packet details pane. Select the first TLS packet, labeled Client Hello. Observe the traffic captured in the top Wireshark packet list pane.
Observe the certificate information provided. Expand Secure Sockets Layer, TLS, Handshake Protocol, and Certificates to view SSL/TLS details. Select the third TLS packet, labeled Certificate, Server Key Exchange, Server Hello Done. Observe the packet details in the middle Wireshark packet details pane.Īctivity 6 - Analyze SSL/TLS Certificate Traffic. Select the second TLS packet, labeled Server Hello. This is the server TCP acknowledgement of receiving the Client Hello request.Īctivity 5 - Analyze SSL/TLS Server Hello Traffic Select the next packet, labeled TCP ACK. Observe the Cipher Suites and Extensions supported. Expand Secure Sockets Layer, TLS, and Handshake Protocol to view SSL/TLS details. Also notice that the Ethernet II, Internet Protocol Version 4, and Transmission Control Protocol values are consistent with the TCP connection analyzed in Activity 3. Notice that it is an Ethernet II / Internet Protocol Version 4 / Transmission Control Protocol / Secure Sockets Layer frame. Observe the packet details in the middle Wireshark packet details pane. Select the first TLS packet, labeled Client Hello. Observe the traffic captured in the top Wireshark packet list pane. Wireshark https vs http mac#
Note that all of the packets for this connection will have matching MAC addresses, IP addresses, and port numbers.Īctivity 4 - Analyze SSL/TLS Client Hello Traffic Notice that it is a dynamic port selected for this HTTPS connection.
Expand Transmission Control Protocol to view TCP details. Notice that the destination address is the IP address of the HTTPS server. Notice that the source address is your IP address. Expand Internet Protocol Version 4 to view IP details. You can use ipconfig /all and arp -a to confirm. The destination should be your default gateway's MAC address and the source should be your MAC address. Observe the Destination and Source fields. Expand Ethernet II to view Ethernet details. 
Notice that it is an Ethernet II / Internet Protocol Version 4 / Transmission Control Protocol frame.

The first three packets (TCP SYN, TCP SYN/ACK, TCP ACK) are the TCP three way handshake.
To view all related traffic for this connection, change the filter to ip.addr =, where is the destination address of the HTTP packet.Īctivity 3 - Analyze TCP Connection Traffic. Select the first TLS packet labeled Client Hello. 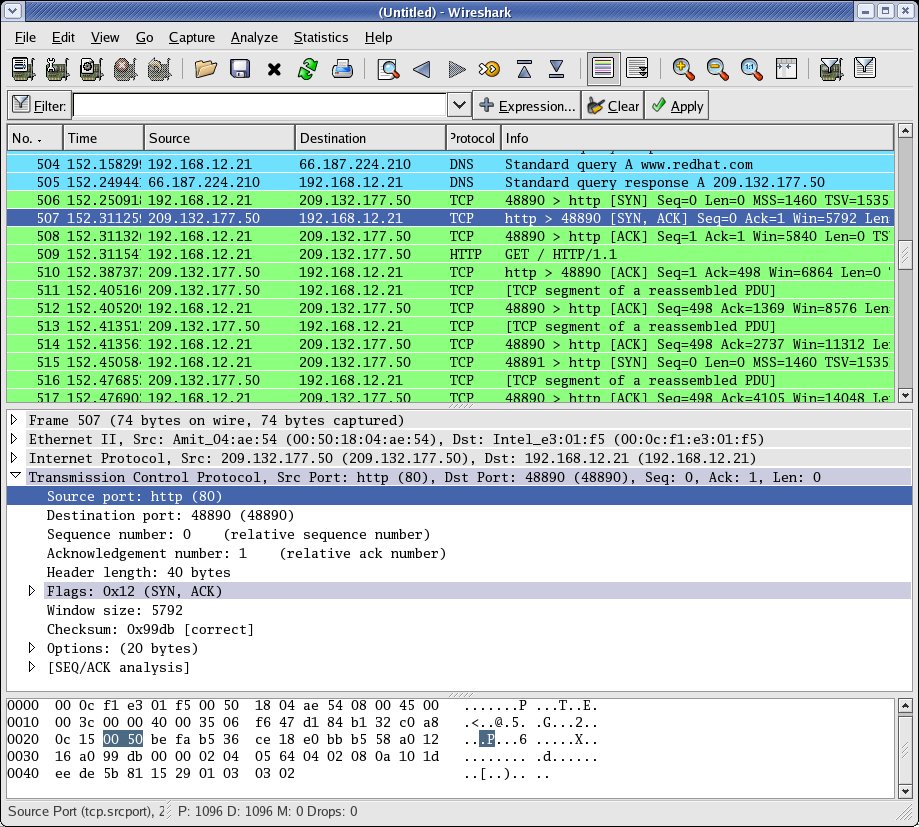
To view only HTTPS traffic, type ssl (lower case) in the Filter box and press Enter.
Wireshark https vs http how to#
These activities will show you how to use Wireshark to capture and analyze Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) traffic.Īctivity 1 - Capture HTTPS Traffic Īctivity 2 - Select Destination Traffic
Wireshark https vs http free#
Wireshark is a free and open source packet analyzer used for network troubleshooting and analysis. 11 Activity 9 - Analyze HTTPS Encrypted Data Exchange.10 Activity 8 - Analyze SSL/TLS New Session Ticket Traffic.9 Activity 7 - Analyze SSL/TLS Client Key Exchange Traffic.8 Activity 6 - Analyze SSL/TLS Certificate Traffic.7 Activity 5 - Analyze SSL/TLS Server Hello Traffic.6 Activity 4 - Analyze SSL/TLS Client Hello Traffic.5 Activity 3 - Analyze TCP Connection Traffic.4 Activity 2 - Select Destination Traffic.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
